Common test methods for water absorption of textiles
Common test methods for water absorption of textiles
Introduction: Water absorption is one of the important indicators of textile testing. Encyclopedia summarizes the test methods that I know. The
commonly used test methods are as follows:
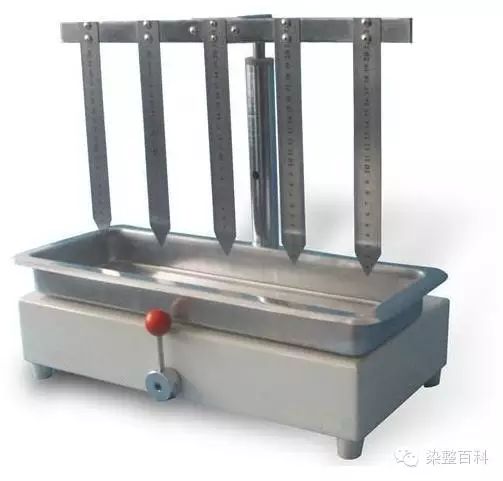
1. Capillary effect method: Capillary effect, that is, capillary effect. Capillary effect test is generally used to detect the quality of textile
pre-treatment. In particular, the two flat-width dyeing methods of roller dyeing and pad dyeing, the uniformity of the water absorption of the
left, middle and right parts of the pre-treatment, as well as the uniformity of the water absorption of the inner, middle and outer parts of the
cheese yarn before dyeing, are generally tested by the capillary effect method. The specific method is: a piece of fabric or yarn of a specified
width is hung and fixed, and a piece is placed in water at a specified temperature or 0.5% potassium permanganate solution. The height of the
water or potassium permanganate solution rising within a specified time, or the time required to rise to the specified height, is tested. The test
results are expressed in cm or seconds. The equipment is relatively simple:

2. Water drip method:
The water drip method is generally used for rapid detection of water absorption of textiles. For example, when a third party inspects the goods,
the water drip method can be used on-site to quickly test the water absorption of textiles. The specific method is: drop a drop of water on the
textile at a specified height, and use a stopwatch to record the time it takes for all the water drops to be absorbed, expressed in seconds. (1ml is
about 18-20 drops, so 1 drop of water is about 0.05ml.) For customers with more stringent requirements, the drip method will require
instantaneous absorption (less than 1 second). There is no need to post the equipment for the drip method! (Save everyone's traffic, it doesn't
matter to the rich)
3. Sedimentation method: The sedimentation method is to test the time it takes for a specified area of fabric to sink into the water. For example,
the water absorption test method of the national standard towel is the sedimentation method. The specific method is: cut off the specified
number of fabrics of specified areas at different parts, and then put them into the water at a specified height, and use a stopwatch to record
the time it takes for the fabric to completely sink into the water. Remember, it must be completely sunk into the water. The sedimentation
method is also expressed in seconds. The smaller the value, the better the water absorption. If it exceeds 60 seconds, it is generally expressed
as >60 seconds. The sedimentation method can be tested with a beaker, and no longer pictured.
4. Water absorption rate method 1:
To make up for the lack of clear encyclopedia language expression, let's look at the picture first:


The above three pictures are from the American standard ASTM D4772 water absorption test method. The principle is to pour a specified
amount of water (usually 50ml) on a fabric of a specified area at a specified height and a specified time, and then collect the unabsorbed water
and calculate the amount of water absorbed by the fabric, expressed as a percentage. If all is absorbed, it is 100%.
5. Water absorption rate method 2:
This method is similar to the previous method. The difference is that it puts a specified weight of fabric into the water, takes it out and places it
at a specified temperature and humidity until it stops dripping or the quality reaches the specified deviation. The amount of water absorbed is
weighed, which is also expressed as a percentage, but this value is generally greater than 100%. For moisture-absorbing and quick-drying
fabrics, their moisture absorption effect can be tested by this method.
Well, the above are the only methods I know. If you have more test methods, please leave a message or message me.




